Introduction
In moment’s ultra modern world nearly everything we do — shopping, banking, studying, or fraternizing happens online.While this has made life more accessible, it has also opened the door to new risks.Cyber culprits are constantly chancing ways to steal data, spread malware, and exploit security gaps. This is where cybersecurity comes in. Cybersecurity is the practice of guarding computer systems, networks, and sensitive data from digital attacks and unauthorized access by employing various technologies, processes, and swish practices. It aims to help cyberattacks like malware and phishing, icing the confidentiality, integrity, and vacuity of information while minimizing the trouble and impact of cyber incidents on individualities and organizations.It’s no longer just a concern for IT professionals it affects individualities, businesses, and indeed governments. As cyberattacks grow in number and complication, understanding cybersecurity has become a necessity for everyone who uses technology.
Why are we talking about Cybersecurity?
- In 1999- Computers of a US Department of Defense division are installed with a ‘ backdoor’ on its waiters
- In 2000- Yahoo!, Amazon, Buy.com, CNN.com, eBay, E * Trade, ZDNet websites hit with massive DoS attack
- In 2017- ‘ WannaCry’ ransomware attack, which encrypts data and demands rescue in the Bitcoin
- In 2019- Facebook’s( about) 540 million records were published on Amazon’s pall computing service

What’s Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the protection of systems, networks, operations and programs from cyber attacks.These Cyber-attacks tend to pierce, change or indeed destroy sensitive information to the extent of exacting plutocrats from druggies or causally intrude a normal business process. Cybersecurity is not just about technology it also involves mindfulness, safe practices, and programs that insure the digital world remains secure for individuals, businesses, and governments.
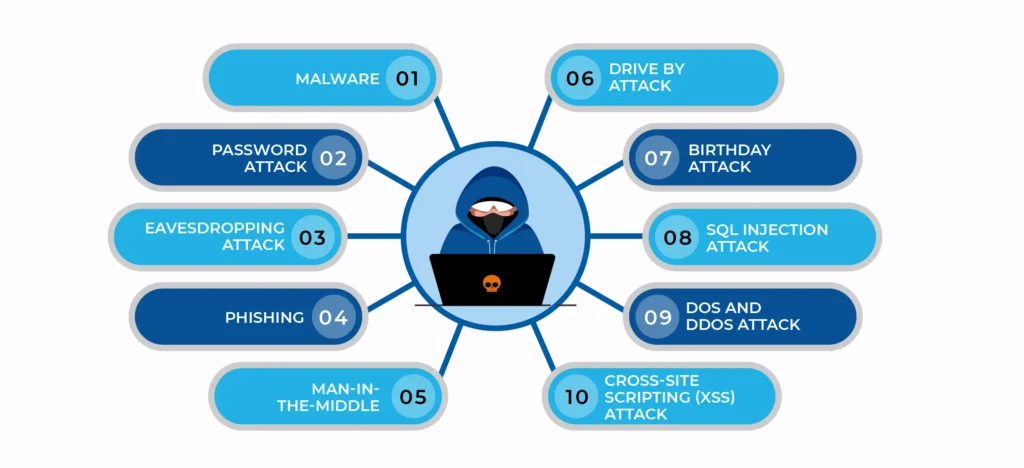
Common Cyber Threats
As our dependence on technology grows, so do the styles cyber criminals use to exploit it. Then are some of the most common cyber pitfalls everyone should be apprehensive of:-
1.Malware( vicious Software)
- Software designed to damage or disrupt a system.
- Includes contagions, worms, Trojans, and spyware.
- illustration A contagion that deletes lines or slows down your computer.
2.Ransomware
- Ransomware is a type of malicious software that locks or encrypts your files and then demands money (a “ransom”) to give back access.
- A real-world example is the 2017 WannaCry attack, which spread across the globe and disrupted hospitals, businesses, and government organizations by making their data completely inaccessible until a ransom was paid.
3.Phishing
- Fake emails, dispatches, or websites designed to trick people into participating in sensitive information like watchwords or bank details.
- illustration An dispatch pretending to be from your bank asking for login credentials.
4.Data Breaches
- Unauthorized access to nonpublic data similar to particular information, fiscal records, or login details.
- illustration Leaks of client data from large companies.
5.Identity Theft
- When bushwhackers steal particular details to impersonate someone for fraud or illegal conditioning.
- Example: Using stolen credit card details to make purchases.
6.Denial- of- Service( DoS) Attacks
- Overfilling a garçon or network with business to make it unapproachable to druggies.
- Example: Taking down a website by submerging it with fake requests.
7.Bigwig pitfalls
- Pitfalls that come from within an association, frequently by workers misusing access to sensitive information.
- illustration An hand oohing company data to challengers.
Why Cybersecurity is Important

In moment’s connected world, cybersecurity is no longer voluntary — it is essential. Every existent, business, and government relies on digital systems to serve, and a single attack can beget serious damage. Then are some crucial reasons why cybersecurity matters:
1.Protects Personal Data
- Cybersecurity keeps our private information—like passwords, bank details, Aadhaar numbers, and even medical records—safe from falling into the wrong hands.
- Without proper protection, this data could be stolen and misused for fraud, scams, or even identity theft.
2.Secures Businesses and Associations
- Companies store client information, fiscal records, and trade secrets.
- A cyberattack can lead to fiscal losses, reputational damage, and indeed legal consequences.
3.Ensures Financial Safety
- Online banking, UPI, and digital holdalls are popular targets for hackers.
- Strong cybersecurity prevents theft of plutocrats through swindles or playing attempts.
4.Protects National Security
- Governments store largely nonpublic data related to defense, structure, and citizens.
- Cyberattacks on critical systems can hang public security.
5.Maintains Trust in Technology
- People feel more confident using digital platforms—whether for payments, shopping, or staying connected—when they know their data is safe. Strong cybersecurity builds that trust.
- Without it, people would hesitate to use online services, and the progress of digital systems could slow down or even stop.
Best Practices for Cyber Safety
Staying safe online does not always bear advanced specialized knowledge — small habits and smart practices can make a big difference. Then are some of the most effective ways to cover yourself in cyberspace:
1.Use Strong and Unique watchwords
- produce watchwords with a blend of letters, figures, and special characters.
- Avoid using the same word for multiple accounts.
- Use a word director if demanded.
2.Enable Multi-Factor Authentication( MFA)
Add a redundant sub caste of security by taking an alternate step( like OTP, point, or dispatch law) in addition to your word.
3.Keep Software and bias streamlined
- Regular updates fix security excrescencies and keep hackers from exploiting vulnerabilities.
- Always contemporize your operating system, apps, and antivirus software.
- Be Careful with Links and Emails
4.Be Careful with Links and Emails
- Do not click on suspicious links or attachments in emails, dispatches, or pop- ups.
- corroborate the sender before participating in any information.
5.Use Secure Networks
- Avoid using public Wi- Fi for banking or sensitive conditioning.
- still, use a Virtual Private Network( VPN) for a safer connection, If demanded.
6.Provisory Your Data
- Regularly provisory important lines to external drives or secure pall storehouse.
- This ensures you do not lose data in case of ransomware or system failure.
7.Protect Personal Information on Social Media
- Limit the quantum of particular data you partake online.
- Acclimate sequestration settings to control who can see your information.
8.Install and Update Security Tools
- Use antivirus, firewalls, and anti- malware tools for spare protection.
- Schedule regular system reviews.

Emerging Trends in Cybersecurity
- As technology grows smarter, cyber threats are also becoming more advanced. Hackers keep finding new ways to attack, which means cybersecurity must keep evolving too.
- To stay one step ahead, experts are constantly developing new tools, strategies, and methods to protect people, businesses, and governments from these threats.
1.Artificial Intelligence( AI) & Machine literacy( ML)
- AI is being used to describe unusual patterns, identify pitfalls briskly, and respond in real time.
- Hackers are also using AI to produce more advanced phishing attacks and malware.
2.Zero Trust Security Model
- Rather than automatically trusting druggies inside a network, this model verifies every access attempt.
- Principle “ no way trust, always corroborate. ”
- Helps help bigwig pitfalls and unauthorized access.
3.Cloud Security Challenges
- With the rise of all services( Google Drive, AWS, Microsoft Azure), securing data in the pall has come critical.
- Focus areas are encryption, access control, and compliance with data protection laws.
4.Internet of effects( IoT) Security
- Devices like smart TVs, fitness bands, and home sidekicks are connected to the internet.
- These frequently warrant strong security, making them targets for hackers.
5.Cybersecurity robotization
- Automated systems help security brigades respond to pitfalls briskly without homemade intervention.
- This reduces mortal error and pets up discovery.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is no longer just a technical matter—it affects our daily lives. From the first backdoors and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks in the 1990s to massive ransomware outbreaks like WannaCry and today’s large-scale data breaches, the risks have only multiplied.Cyberattacks don’t just target machines—they steal personal information, disrupt businesses, and even put national security at risk.The good news? We can all play a role in staying safe online. Simple steps like using strong and unique passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication, keeping our devices updated, practicing good cyber hygiene, and being cautious with suspicious emails or links can go a long way in protecting us.
As technology keeps advancing, new challenges will arise. But with awareness, safe practices, and consistent vigilance, we can protect ourselves and help build a safer, more trusted digital world.