Introduction
In the moment’s hyperactive- connected digital terrain, associations are no longer confined to traditional office walls. Workers work from home, operations run in the pall, and data flows between in numerous biases across the globe. While this brings inflexibility and invention, it also creates vulnerabilities. Traditional border- grounded security models which assumed that everything inside the commercial network was safe — are no longer sufficient. This is where Zero Trust Security comes into play.
Zero Trust Security has surfaced as a revolutionary approach to guarding digital means. Rather than assuming trust grounded on position or network boundaries, it continuously verifies every stoner, device, and operation, anyhow of whether they’re inside or outside the association. In simple terms no way to trust, always corroborate.
What is Zero Trust Security?
Zero Trust Security is a cybersecurity frame that requires strict verification for every stoner and device trying to pierce coffers within a network. The core idea is that no bone is innately trusted — not indeed workers or bias inside the network border.
The concept was introduced by Forrester Research critic John Kindervag in 2010. He argued that trust, formerly granted implicitly, came with a significant vulnerability. By removing this supposition and treating every request as potentially vicious, Zero Trust reduces the chances of data breaches and bigwig pitfalls.
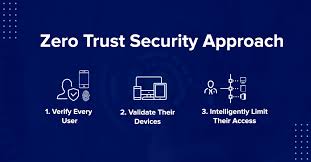
Key Principles of Zero Trust
Here are the core principles of Zero Trust explained in a clear way:
- Verify Explicitly
Every stoner and device must be authenticated and authorized before penetrating coffers. Verification relies on multiple signals similar as stoner identity, device health, geolocation, and geste patterns
- Least-Privilege Access
Users should only have access to the data and systems they need to perform their jobs — nothing further. By limiting boons, the damage caused by compromised accounts can be minimized.
- Assume Breach
Zero Trust assumes that bushwhackers may formerly be inside the network. Rather than fastening solely on keeping pitfalls out, it emphasizes constraint and minimizing side movement.

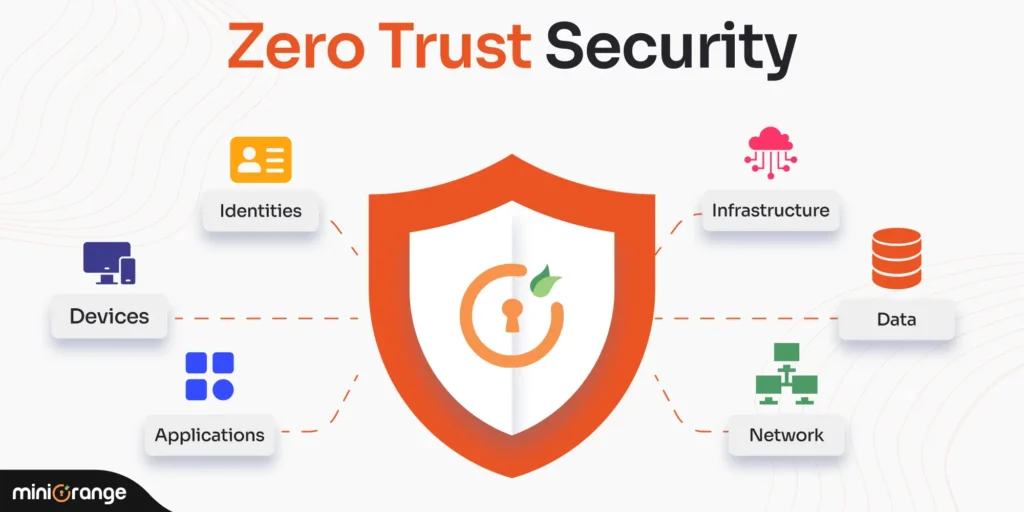
Core Components of Zero Trust Architecture
Enforcing Zero Trust involves several connected technologies and practices:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM):Tools like multi-factor authentication( MFA) insure that druggies are who they claim to be.
- Device Security:Devices must be vindicated and covered for compliance before being granted access.
- Micro-Segmentation:Networks are divided into lower parts to limit unauthorized access.
- Encryption:Data is translated both in conveyance and at rest to cover against interception.
- Continuous Monitoring and Analytics:Real- time perceptivity helps describe unusual exertion that might indicate a breach.
- Automation and Orchestration:Automated responses reduce the time between discovery and mitigation of pitfalls.
Why Zero Trust Matters Today
The traditional” castle and culvert” approach worked when associations had a well- defined border, similar to office structures and on- deck waiters. Still, the rise of pall computing, remote work, mobile bias, and IoT has blurred these boundaries. Bushwhackers no longer need to transgress the border; they can exploit weak credentials, phishing emails, or relaxed devices.
Statistics punctuate the urgency:
- According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average cost of a breach in 2023 was over$ 4.5 million.
- further than 80% of breaches involved weak or stolen passwords.
Zero Trust addresses these challenges by icing security at every access point, making it harder for bushwhackers to move indirectly formerly outside.
Benefits of Zero Trust Security
- Enhanced Data Protection
Sensitive information, whether stored in pall operations or on- demesne databases, remains secure through encryption, access control, and monitoring
- Reduced threat of Insider Threats
Workers and contractors only pierce what they need, precluding accidental or vicious abuse of data.
- More Visibility and Control
Zero Trust provides associations with perceptivity into who’s penetrating data, from where, and under what conditions.
- Advanced Compliance
Numerous diligence bears strict data security norms. Zero Trust helps meet non supervisory conditions like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
- Rigidity to ultramodern Work surroundings
With mongrel and remote work getting the norm, Zero Trust ensures secure access from any position and device.

Challenges in Implementing Zero Trust
While Zero Trust offers significant benefits, associations frequently face hurdles during relinquishment
- Complexity Shifting from traditional models to Zero Trust requires significant architectural changes.
- Cost perpetration can be precious, especially for small associations with limited coffers.
- Cultural Resistance workers may find nonstop verification inconvenient, leading to pushback.
- Integration Issues Being heritage systems may not seamlessly align with Zero Trust principles.
Despite these challenges, gradational perpetration and proper planning can help overcome them.
Steps to Implement Zero Trust Security
Associations can adopt Zero Trust in phases to ensure smooth transition:
- Identify Sensitive Data and means
Begin by mapping critical coffers that need protection, similar as client databases, fiscal records, and intellectual property.
- Define Access programs
Establish who should pierce what data, under what conditions, and for how long.
- Apply Strong Identity Controls
Use MFA, single sign- on( SSO), and adaptive authentication to strengthen security.
- Member the Network Apply micro-segmentation to circumscribe side movement of bushwhackers.
- Examiner Continuously
Emplace monitoring tools to describe anomalies and apply programs in real- time.
- Automate Responses
Use AI- driven tools to automatically contain pitfalls and help breaches from raising.
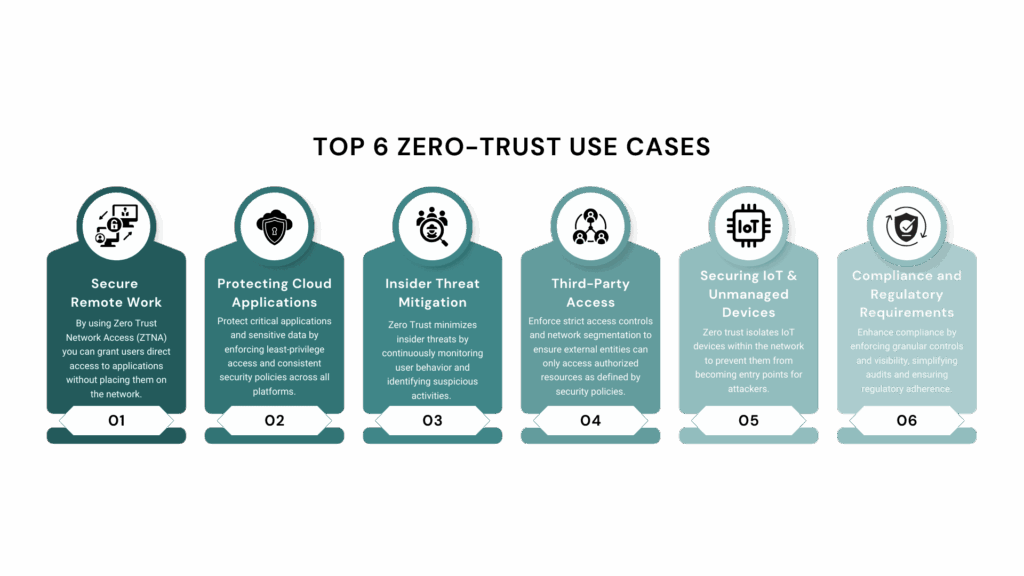
Real-World Applications of Zero Trust
Zero Trust is not just a proposition, it’s being espoused by associations worldwide.
- Government Agencies The U.S. government has commanded Zero Trust relinquishment across civil agencies to guard public security.
- Healthcare Hospitals use Zero Trust to cover case records and misbehave with HIPAA regulations.
- Financial Services Banks calculate on Zero Trust to secure deals and help fraud.
- Enterprise Companies like Google enforced a Zero Trust model called BeyondCorp, enabling workers to work securely from anywhere.
The Future of Zero Trust Security
As cyber pitfalls evolve, Zero Trust will continue to gain traction. Unborn; advancements may include:
- AI and Machine Learning: Smarter trouble discovery and automated policy adaptations.
- Zero Trust for IoT: icing secure communication between billions of connected biases.
- Global norms: further unified fabrics for diligence worldwide.
Eventually, Zero Trust will probably become the dereliction security model for ultramodern associations, much like seatbelts are now standard in buses .

Conclusion
Zero Trust Security is further than just a cybersecurity buzzword — it is a practical frame that addresses the realities of the moment’s digital geography. By barring implicit trust, administering least- honor access, and continuously covering druggies and bias, Zero Trust provides a robust defense against both external and internal pitfalls.
While the trip to Zero Trust may be complex, its benefits far overweight the challenges. Organizations that borrow it are more equipped to guard data, make client trust, and thrive in a digital-first world. In a period where cyberattacks are not a question of if but when, Zero Trust is not just an option it’s a necessity.